Dog Not Eating Food? Causes & Simple Solutions Guide

Dog Not Eating Food? Here’s What You Should Know
Is your dog not eating food, leaving you worried and confused? This behavior can be triggered by various reasons—some minor, others more serious. Understanding why your dog is refusing food is essential for their health and your peace of mind.
Dogs are usually enthusiastic eaters, so when a dog suddenly stops eating food, it’s a cause for concern. Common reasons include stress, illness, or environmental changes. Even something as simple as disliking a new dog food brand can lead to a loss of appetite.
Identifying the root cause when your dog is not eating food helps you take the right steps to solve the issue. In this article, we’ll explore why dogs refuse food and share practical tips to help your furry friend regain their appetite. Acting early can protect your dog’s health and bring back happy mealtimes.
Common Reasons
Dogs sometimes refuse to eat, and this can be concerning for pet owners. There are several common reasons why a dog might not eat its food. Understanding these reasons helps in identifying the problem and finding a solution. It is important to consider various factors such as health issues, stress, anxiety, and changes in routine. Addressing these factors can help your dog regain its appetite and ensure its well-being.
Health Issues
Health problems are a frequent cause for a dog’s loss of appetite. Dental issues can make it painful for dogs to chew. Look for signs like swollen gums or drooling. Digestive problems, such as an upset stomach or constipation, can also lead to reduced eating. Infections or diseases might cause discomfort, leading to decreased food intake. Parasites like worms can affect a dog’s nutritional absorption, causing hunger loss.
Here’s a quick checklist for common health issues:
- Painful or swollen gums
- Upset stomach or constipation
- Signs of infection
- Presence of parasites
If your dog shows any of these signs, a visit to the vet is important. Early detection and treatment can prevent serious health problems.
Stress Or Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can affect a dog’s eating habits. Changes in the environment, like moving to a new house, might stress them. Loud noises, such as thunderstorms, can make dogs anxious. Separation anxiety when left alone can also cause a decrease in appetite. Fear of other pets or people can lead to stress-related eating issues.
Signs of stress or anxiety include:
- Excessive barking or whining
- Trembling or hiding
- Destructive behavior
- Pacing or restlessness
Creating a calm environment may help reduce stress. Providing comfort and reassurance can encourage your dog to eat again.
Changes In Routine
Routine changes often impact a dog’s eating habits. Alterations in feeding times can confuse them, leading to skipped meals. Switching food brands might cause a dog to refuse to eat. Changes in daily activities like exercise schedules can affect appetite.
Consider these possible changes in routine:
- Feeding at different times
- Introducing new food brands
- Changing exercise routines
Gradually introducing changes can help your dog adjust. Maintaining consistency in routine is key to keeping your dog comfortable and willing to eat.
Health Concerns
Dogs sometimes refuse food, causing worries for pet owners. Understanding why a dog isn’t eating is crucial. Health issues often cause this behavior. Identifying the problem can help address it quickly. Let’s explore some health concerns that might cause a dog to stop eating.
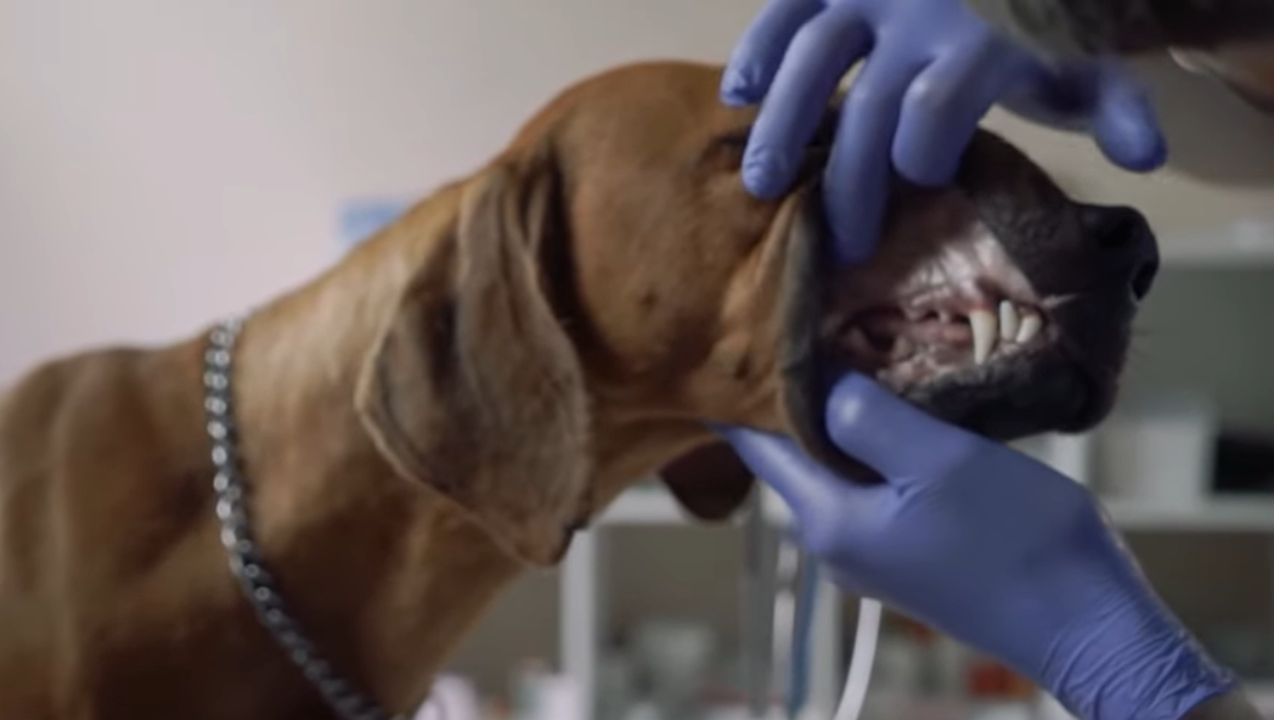
Dental Problems
Dental issues can make eating painful for dogs. Problems like tooth decay or gum disease are common culprits. A dog’s mouth can hurt, leading to eating refusal.
Signs of dental problems include:
- Bad breath
- Swollen gums
- Loose teeth
- Drooling more than usual
Regular dental check-ups can prevent these issues. A vet can spot problems early. Dental cleanings and home care can help maintain oral health. For dogs already in pain, soft foods may be easier to eat. Always consult a vet for severe dental issues.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Digestive problems can also stop a dog from eating. Stomach aches, bloating, or diarrhea might be to blame. These issues can make eating uncomfortable.
Common gastrointestinal problems:
- Upset stomach
- Intestinal blockage
- Gastritis
- Pancreatitis
Monitoring a dog’s eating habits can help identify issues. Pay attention to vomiting or changes in stool. A vet can provide treatments like special diets or medications. Prompt action can prevent more serious health problems.
Infections
Infections can lead to a loss of appetite in dogs. Viral, bacterial, or fungal infections can affect a dog’s desire to eat. These infections often come with other symptoms.
Possible infection symptoms:
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Coughing or sneezing
- Swollen lymph nodes
Veterinary care is essential for infections. Antibiotics or other medications may be needed. Regular vaccinations can help prevent some infections. Keeping a dog healthy involves both prevention and treatment.
Behavioral Factors
Dogs sometimes stop eating their food. This can worry pet owners. There are many reasons for this behavior. Behavioral factors are one of the main reasons. Understanding these can help solve the issue. It is important to know why dogs refuse food. It helps maintain their health and happiness.
Picky Eaters
Some dogs are picky eaters. They may not like certain foods. This can be frustrating for owners. Dogs have different tastes. They might like one food and dislike another. Here are some reasons dogs can become picky:
- Taste Preferences: Dogs have specific likes and dislikes.
- Texture Issues: Some dogs prefer softer or crunchier food.
- Routine Changes: A sudden change in diet can make dogs refuse food.
To help picky eaters, try rotating different flavors. Introduce new textures gradually. Observe your dog’s reaction. If they show interest, continue with that type of food. Consistency can also help. Keep mealtime routines stable. This can make dogs feel comfortable with their food.
Food Sensitivities
Some dogs have food sensitivities. This means certain foods upset their stomach. It can lead to a refusal of food. Common symptoms include vomiting and diarrhea. These can make dogs associate food with discomfort. Here are some common food sensitivities in dogs:
| Food Type | Sensitivity Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Dairy | Diarrhea, bloating |
| Grains | Itchy skin, ear infections |
| Chicken | Vomiting, gas |
If you suspect food sensitivities, consult a vet. They can recommend a special diet. This will help your dog eat comfortably. Always monitor your dog’s reaction to new foods. This ensures they enjoy their meals without discomfort.
Environmental Changes
Dogs are sensitive to environmental changes. New surroundings can affect their appetite. Moving to a new home or having new people around can cause stress. This can lead to a decline in eating. Dogs may need time to adjust. Here are some changes that can affect a dog’s eating habits:
- New Home: Unfamiliar surroundings can make dogs feel anxious.
- Routine Alterations: Changes in the daily schedule can confuse dogs.
- Presence of Strangers: New faces can cause stress.
To help your dog adjust, create a calm environment. Stick to regular feeding times. Make sure their eating area is quiet and comfortable. Gradually introduce changes. This helps dogs feel safe and more willing to eat. Patience is key. Give your dog time to adapt to new situations.
Dietary Changes
Dogs sometimes refuse to eat their food, which can be worrying for pet owners. Understanding why your dog isn’t eating is crucial. Dietary changes may help. Knowing what adjustments to make can ensure your dog stays healthy and happy. Let’s explore how new food introductions, feeding schedule adjustments, and portion control can aid in resolving this issue.

New Food Introductions
Introducing new food to your dog can be a challenge. Dogs are creatures of habit. Sudden changes in diet may cause them to reject food. To help your dog adapt, consider the following steps:
- Gradually mix new food with the old one. This helps them adjust.
- Monitor for allergic reactions or digestive issues.
- Choose food with high-quality ingredients. This can increase interest.
Here’s a simple table to help with new food introduction:
| Day | Old Food (%) | Dog Not Eating Food(%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | 75 | 25 |
| 4-6 | 50 | 50 |
| 7-9 | 25 | 75 |
| 10+ | 0 | 100 |
Following these steps can make the transition smoother and increase the chances of acceptance.
Feeding Schedule Adjustments
Adjusting the feeding schedule can help if your dog is not eating. Dogs thrive on routine. A consistent schedule can improve their eating habits. Consider the following tips:
- Feed at the same time each day.
- Observe your dog’s activity levels. Adjust feeding times accordingly.
- Avoid feeding late at night. This can affect digestion.
Consistency is key. A set schedule helps your dog anticipate meals. This can reduce anxiety around feeding times.
If problems persist, consult a vet. They can provide tailored advice.
Portion Control
Proper portion control is vital for your dog’s health. Overfeeding can lead to weight issues. Underfeeding can cause malnutrition. To ensure balanced portions, keep these points in mind:
- Use a measuring cup to portion food accurately.
- Consider your dog’s weight and activity level.
- Monitor weight regularly. Adjust portions as needed.
Here’s a simple guide for portion control:
| Dog Weight (kg) | Daily Food Amount (g) |
|---|---|
| 5-10 | 100-200 |
| 10-20 | 200-400 |
| 20-30 | 400-600 |
| 30+ | 600+ |
Adjust portions based on age and breed. With careful monitoring, your dog can enjoy a balanced diet.
Signs Of Illness
Dogs sometimes refuse food, causing their owners to worry. This can be a sign of illness. It’s important to watch for other symptoms that may indicate health issues. Changes in behavior, energy levels, or digestion can give clues. Understanding these signs helps ensure the dog’s well-being.
Lethargy
Lethargy in dogs means low energy or tiredness. It’s more than just a lazy day. A lethargic dog might sleep a lot or not want to play. This can be a sign of illness. It’s important to notice how long the lethargy lasts.
Signs of lethargy include:
- Sleeping more than usual.
- Not interested in toys or walks.
- Slow movements or reactions.
Contact a vet if the dog is lethargic for more than a day. It could be a sign of a serious condition. Always keep track of their daily energy and activity levels.
Vomiting
Vomiting is a clear sign that something is wrong with a dog. Occasional vomiting may not be serious. But frequent vomiting needs attention. It’s important to check for other symptoms.
Common causes include:
- Eating something toxic.
- Stomach infections.
- Motion sickness.
Watch the dog’s behavior after vomiting. If the dog is weak or refuses food, it may need a vet’s care. Monitor how often vomiting occurs and note any changes in diet or environment.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea in dogs can occur due to many reasons. It can be a result of a change in diet or stress. Persistent diarrhea is a cause for concern. It can lead to dehydration.
Causes of diarrhea include:
- Diet changes or food intolerance.
- Infections or parasites.
- Anxiety or stress.
Keep an eye on the frequency and consistency of bowel movements. If diarrhea lasts more than a day, seek veterinary advice. Dogs can lose fluids quickly, leading to serious health issues.
Consulting A Vet
Dogs are known for their love of food. Yet, sometimes they refuse to eat. This can be worrying for pet owners. Loss of appetite may signal a health problem. Consulting a vet becomes crucial. A vet can pinpoint the reason and suggest solutions. This helps ensure your dog stays healthy and happy.
When To Seek Help
It’s important to know when your dog needs a vet’s attention. Persistent refusal to eat is a major sign. If your dog hasn’t eaten for more than 24 hours, contact a vet. Other signs include:
- Vomiting or diarrhea alongside loss of appetite.
- Lethargy or weakness with no interest in food.
- Sudden weight loss despite reduced food intake.
- Changes in behavior, like aggression or withdrawal.
These symptoms might indicate serious issues. Timely consultation can prevent complications. Early intervention is key to your dog’s recovery. Vets can identify problems quickly. They use tests and exams to diagnose effectively.
What To Expect
Visiting a vet involves several steps. Initial examination is the first. The vet checks your dog’s vital signs. This includes temperature, pulse, and breathing rate. They may ask about recent behavior changes. Diagnostic tests might be necessary. Blood tests, X-rays, or ultrasounds can uncover hidden issues. Vets use these to understand underlying causes.
Once diagnosed, treatment options are discussed. Medications might be prescribed. Special diets could be recommended. In some cases, further tests may be required. Vets aim to address the root cause. This ensures effective treatment and recovery.
Follow-up Care
After initial treatment, follow-up care is vital. Vets often schedule check-ups. These ensure your dog responds well to treatment. Monitoring progress helps in adjusting care plans. Vets may suggest dietary changes or medication adjustments. Home care is equally important. Ensure your dog gets enough rest and a comfortable environment.
Keep an eye on any changes in behavior or appetite. Report these to the vet promptly. Continued care prevents relapses. It also helps maintain your dog’s overall health. Regular vet visits keep your dog in the best condition. They provide peace of mind for pet owners.
Encouraging Eating
Dogs sometimes refuse to eat. It can be worrying for owners. Understanding why is key. Encouraging eating can help. Simple tricks make a big difference. Let’s explore ways to get your dog eating again.
Food Toppers
Food toppers can make meals appealing. Dogs love new tastes. Adding food toppers is a great way to make meals inviting. You can use chicken broth or beef gravy. These enhance flavor and smell.
- Chicken broth – Adds flavor without too many calories.
- Beef gravy – Rich taste that dogs enjoy.
- Pumpkin puree – Good for digestion and adds sweetness.
Mixing these with regular food can work wonders. Dogs often respond to changes in taste and texture. Experiment with different toppers. Find what your dog likes best.
Warm Meals
Warm meals can be comforting. Heating food slightly can enhance the aroma. Dogs have sensitive noses. A warm meal can smell more inviting. It’s similar to how humans enjoy warm meals.
Try microwaving food for a few seconds. Ensure it’s not too hot. Warm food is easier to digest. It can also mimic freshly cooked meals. Dogs often show more interest in meals that seem fresh.
Experiment with warmth levels. Some dogs like it just slightly warm. Others prefer it a bit hotter. Adjust according to your dog’s preference. Watch how your dog reacts. This can guide you in warming their meals.
Routine Establishment
Routine is crucial for dogs. Setting a regular feeding time helps. Dogs thrive on predictability. Having meals at the same time daily can encourage eating. It builds expectation and habit.
Create a feeding schedule. Stick to it as much as possible. Consistency is key. Dogs learn to expect food at certain times. This reduces anxiety and improves appetite.
Observe your dog’s natural rhythm. Some dogs prefer morning meals. Others may eat better in the evening. Find what works for your pet. Adjust the routine accordingly. This can lead to better eating habits.
Preventive Measures
Many dog owners feel worried when their pet refuses to eat. A change in appetite can be a sign of health issues. It is important to know how to prevent this problem. Preventive measures can help keep your dog healthy and happy. These measures include regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and stress reduction techniques. By following these steps, you can ensure your dog remains in good health.
Regular Check-ups
Regular vet visits are crucial for your dog’s health. Early detection of health problems can save your dog from suffering. It can also save you costly treatments in the future. Here are some important aspects to consider:
- Annual or bi-annual check-ups help monitor overall health.
- Vaccinations and booster shots protect against diseases.
- Dental check-ups prevent oral health issues.
- Routine blood tests detect hidden illnesses.
During these visits, discuss any changes in your dog’s eating habits. The vet can provide guidance or adjustments to your dog’s diet. Regular check-ups help maintain your dog’s well-being and prevent major health issues.
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is vital for your dog’s nutrition. Proper nutrition supports growth, energy, and a healthy immune system. Consider the following when choosing your dog’s diet:
| Nutrient | Importance |
|---|---|
| Proteins | Builds and repairs tissues |
| Fats | Provides energy and supports cell growth |
| Carbohydrates | Source of energy |
| Vitamins and Minerals | Supports various bodily functions |
Choose high-quality food with these nutrients. Consult your vet for advice on portion sizes. Avoid feeding your dog table scraps, as this can lead to obesity and bad habits. A well-balanced diet keeps your dog healthy and helps maintain a normal appetite.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress can affect your dog’s appetite. Reducing stress is important for your pet’s health. Here are some techniques to help your dog relax:
- Regular exercise helps expend energy and reduce anxiety.
- Provide a calm and safe environment.
- Use toys to engage and distract your dog.
- Maintain a consistent daily routine.
Some dogs may need more attention or companionship. Spending quality time with your pet can alleviate stress. If stress persists, consult your vet for further advice. Stress reduction techniques can improve your dog’s mood and appetite.

Frequently Asked Questions: Dog Not Eating Food
What To Do If A Dog Isn’t Eating Food?
Check for any signs of illness and consult a vet. Try offering different food or flavors. Ensure the dog has a comfortable eating environment. Keep their feeding schedule consistent. Monitor their behavior and hydration closely.
When Should I Worry About My Dog Not Eating?
Monitor your dog if they skip meals for more than 24 hours. Check for signs of illness or discomfort. Sudden loss of appetite may indicate health issues. Consult a vet if your dog shows persistent refusal to eat or other symptoms like vomiting, lethargy, or diarrhea.
How Long Is It Okay For A Dog Not To Eat?
A dog can safely go without food for 24 to 48 hours. Beyond that, consult a vet for advice. Puppies and dogs with health issues may need attention sooner. Always ensure they have access to fresh water. If your dog refuses to eat, monitor for signs of illness.
Why Is My Dog Not Eating His Food But Acting Normal All?
Your dog might be bored with their food. Check for changes in routine or environment. Dental issues could also be a cause. Monitor their behavior closely. If the issue persists, consult a veterinarian.
Why Is My Dog Not Eating Its Food?
A dog might skip meals due to stress, illness, or changes in routine. Check for symptoms. Consult a vet.
Conclusion
Understanding why your dog isn’t eating is crucial. It helps maintain their health. Try different foods. Observe their behavior closely. Small changes can make a big difference. Consult a vet if problems persist. They can provide expert advice. Remember, each dog is unique.
What works for one might not work for another. Stay patient and attentive. Your furry friend relies on you. Eating habits can signal bigger issues. Address them early for peace of mind. Keep your pet’s happiness a priority. A healthy dog is a happy dog.







